Table of Contents
Wrinkles
Wrinkles, that are also known as rhytids, are natural lines and creases that appear on the skin as a result of the aging process. They are usually found on areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, hands, and forearms. Different factors like sun exposure, pollutants, and smoking can lead to the formation of wrinkles. Wrinkles can also result due to habitual sleeping positions, loss of body mass, or prolonged immersion in water. There are different treatments for wrinkles based on Invasiveness and Non invasiveness. Each of them is enlisted in this article

Non-invasive Treatments for Wrinkles
Fillers used for the Treatment of Wrinkles

Fillers are used to inject substances into the hypoderm or dermal tissue to enhance the appearance of specific areas, usually the face, for aesthetic purposes mainly for the treatment for wrinkles. As these Fillers are injected into the designated area, it results in the addition of volume beneath the surface of skin by attracting water to it. It causes Filling or Plumping up the treated area that is beneficial for wrinkles. Fillers can be categorized into different types as following:
- Temporary Fillers: Commonly used due to their temporary effect. Substrates like bovine collagen, hyaluronic acid, and agarose gel are reabsorbed by local enzymes.
- Partially Absorbable Fillers: These have an absorbable part (like hyaluronic acid or collagen) and a non-absorbable part (such as synthetic materials like dextran beads).
- Permanent Fillers: Synthetic and intended to be permanent, they are used for volumetric correction of deep defects and are made of materials like acrylics, hydroxyapatite, and silicones.
Peelings:
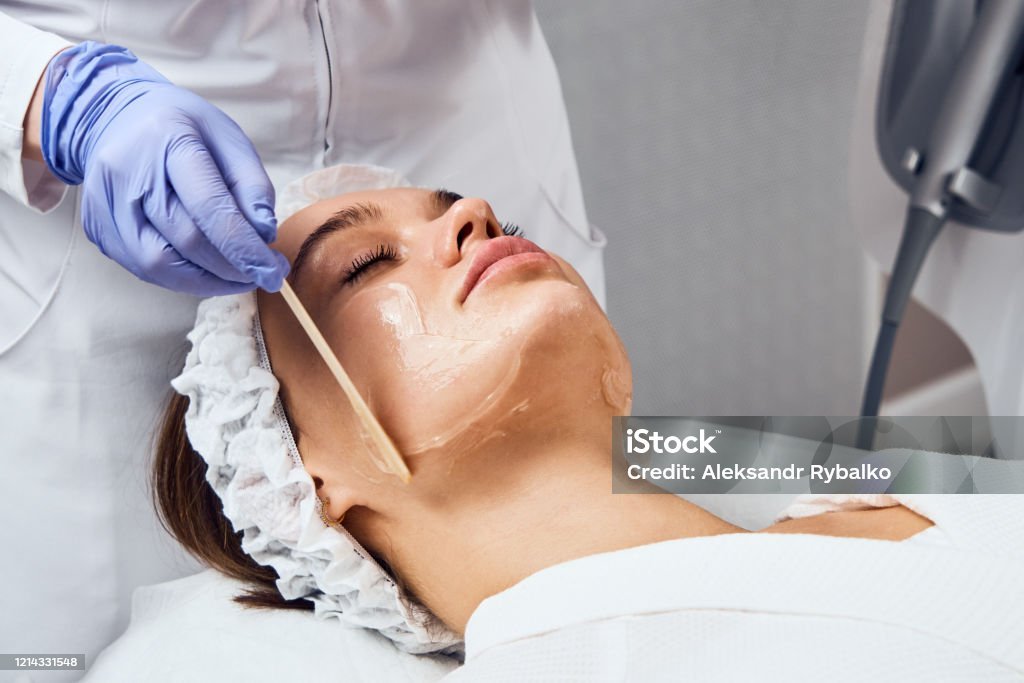
Peeling involves the micro-abrasion of the epidermis or the superficial and medium dermis using chemical or physical agents. Chemical peels causes controlled skin injuries that results in the stimulation of new growth and improved texture and appearance. It’s used to revitalize and rejuvenate the skin and can be classified into:
- Superficial Peels: Superficial peels are used to treat mild skin issues such as acne and pigmentation with minimal downtime. Superficial chemical peels affect the epidermis and stimulate the papillary dermis using acids such as pyruvic, salicylic, and trichloroacetic acid (TCA). These acids work by exfoliating the outermost layer of the skin, promoting the removal of dead skin cells and encouraging the regeneration of new skin cells.
- Pyruvic acid is effective for its keratolytic and antimicrobial properties.
- Salicylic acid is known for its ability to penetrate and clear pores while also being anti-inflammatory.
- TCA helps to remove damaged skin layers, leading to smoother and more even-toned skin. .
- Medium Peels: Medium depth peels address issues such as solar lentigines and superficial scars, requiring longer healing. Using trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and glycolic acid, they penetrate the superficial dermis, exfoliating damaged skin cells and promoting ne cell growth. TCA helps to exfoliate the outer layers of the skin, promoting the removal of damaged skin cells and encouraging new cell growth. Glycolic acid, an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA), further enhances this process by breaking down the bonds between dead skin cells, facilitating their removal and revealing fresher, smoother skin underneath. This combination stimulates collagen production in the superficial dermis, improving skin texture, reducing fine lines, and enhancing overall skin firmness and appearance.
- Deep Peels: Deep peels are used to treat severe photoaging and deep wrinkles by affecting the intermediate dermis with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) at higher concentrations and phenolic-based solutions. These high-concentration peels penetrate deeply into the skin, reaching the intermediate dermis to remove damaged skin layers and promote substantial regeneration. TCA at higher concentration and phenol create a controlled injury that stimulates the production of new collagen and elastin, significantly improving skin texture and reducing deep wrinkles. The process requires significant healing time but results in a dramatic rejuvenation of the skin’s appearance.
Botulinum Toxin:
Botulinum toxin injections are a common treatment for facial wrinkles. The toxin inhibits acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction, causing localized muscle relaxation that smooths the skin and reduces wrinkles. The effects develop fully in two weeks and last for three to four months.
Lasers:
Lasers, such as CO2 and Erbium Yag lasers, are used for non-invasive skin treatments, including aesthetic lesion removal, resurfacing, non-ablative rejuvenation, and hair removal.
- CO2 Laser works by emitting a specific wavelength of infrared light (10,600 nm) that penetrates into the skin that targets the water molecules in the tissue. This interaction cause heat generation creating small controlled areas of thermal damage in the skin. These micro-injuries stimulates the skin’s natural healing process, promoting the production of new collagen and the formation of fresh epidermal cells to replace damaged skin.
- The Erbium YAG Laser is a precise (2940-nm) ablative laser that targets water inside cells more effectively than CO2 lasers. This reduces damage to surrounding tissue, minimizing collagen shrinkage and treating wrinkles more gently. It causes less redness and fewer complications than CO2 lasers due to less heat spreading.
Invasive Treatments for Wrinkles
Restoration and Plastic Surgery:
Restoration and Plastic Surgery:

Plastic surgeons are innovating treatments to address photoaging, pigmentation issues, and skin laxity. While traditional methods such as laser resurfacing and deep peels are effective, they can damage the epidermis and lead to complications like increased sensitivity and dyschromias. In response, less invasive alternatives such as fractionated lasers, radiofrequency heat, and intense pulsed light are gaining popularity.
Additionally, minimally invasive procedures are on the rise, with an expected increase in related devices. Emerging treatments like percutaneous collagen induction aim to promote skin regeneration rather than scar formation, offering a promising approach to improving skin quality and reducing wrinkles with fewer side effects. For more permanent results, invasive treatments include procedures for redistributing fat and volume loss, enhancing skin augmentation and contouring, and performing plastic surgery.
Cosmetic Care for Wrinkles Treatment
Daily Skin Care:
Daily care involves correct sun protection, aesthetic non-invasive procedures, and the use of antioxidants. A healthy lifestyle and avoiding exogenous factors are also crucial for skin health.
Key Molecules in Cosmetology
| Serial Number | Key Molecules | Effect |
| 1 | Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | Known for its antioxidant properties and ability to stimulate collagen production. Common forms in cosmetics include ascorbyl palmitate, magnesium ascorbyl phosphate, and L-ascorbic acid. |
| 2 | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Essential for maintaining membrane homeostasis, influencing gene expression, and regulating inflammatory responses. They also help in treating acne, psoriasis, and dermatitis. |
| 3 | Hyaluronic Acid | A key component of the extracellular matrix, involved in cell adhesion, motility, differentiation, and proliferation. Widely used in cosmetic formulations for its hydrating properties. |
| 4 | Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) | A powerful natural antioxidant that scavenges free radicals, chelates metals, and restores intracellular glutathione levels. |
| 5 | Vitamin E (Tocopherol) | A potent antioxidant that protects against UV-induced damage, reduces erythema and edema, and prevents lipid peroxidation |
| 6 | Retinol (Vitamin A) | Popular in cosmetics for aged skin, it normalizes keratinization and regulates epithelial cell growth, reducing roughness and facial wrinkling. |
Natural Compounds and Herbal Products for Wrinkles Treatment
Phenolic Compounds and Flavonoids:
Phenolic compounds are derived from plants and these compounds have antioxidative properties, protecting against photo-damage and enhancing skin elasticity. Some of these compounds with the potential to treat wrinkles are listed below
- Polypodium Leucotomos and Camellia Sinensis extracts provide protection against UV damage and support overall skin health by acting as antioxidants and reducing inflammation.
- Ellagic Acid, found in berries, prevents the breakdown of dermal elastic fibers in the skin and promotes the production of new elastin.
- Aceriphyllum Rossii extracts help reduce tissue degradation by inhibiting enzyme called matriz metalloproteinases. decreasing tissue degradation.
- Combination Fruit Extracts from sources like pomegranate, ginkgo biloa, fig, and white mulberry are effective at inhibiting collagenase, preserving collagen levels in skin.
- Emblica officinalis, Centella asiatica, Panax ginseng, and Cinnamomum zeylanicum extracts promote the synthesis of collagen fibers, enhancing skin elasticity and firmness.
- Licorice Extract and Raspberry Ketone are used for skin lightening by inhibiting melanin synthesis .
- Origanoside acts as melanin synthesis inhibitor, reducing skin pigmentation.
Topical Effects
Effective cosmetic products should meet specific standards by ensuring the active ingredient can penetrate the stratum corneum, has a known biochemical mechanism of action in target skin cells, and is supported by peer-reviewed, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Among the ingredients, Niacinamide is noted for meeting these standards of cosmeceutical-ingredient analysis.

